GraphQL Requests
Build and execute GraphQL queries and mutations with schema-aware autocomplete
Yaak supports GraphQL alongside REST, gRPC, and WebSocket. Write queries and mutations with autocomplete, explore schemas visually, and chain responses into other requests.
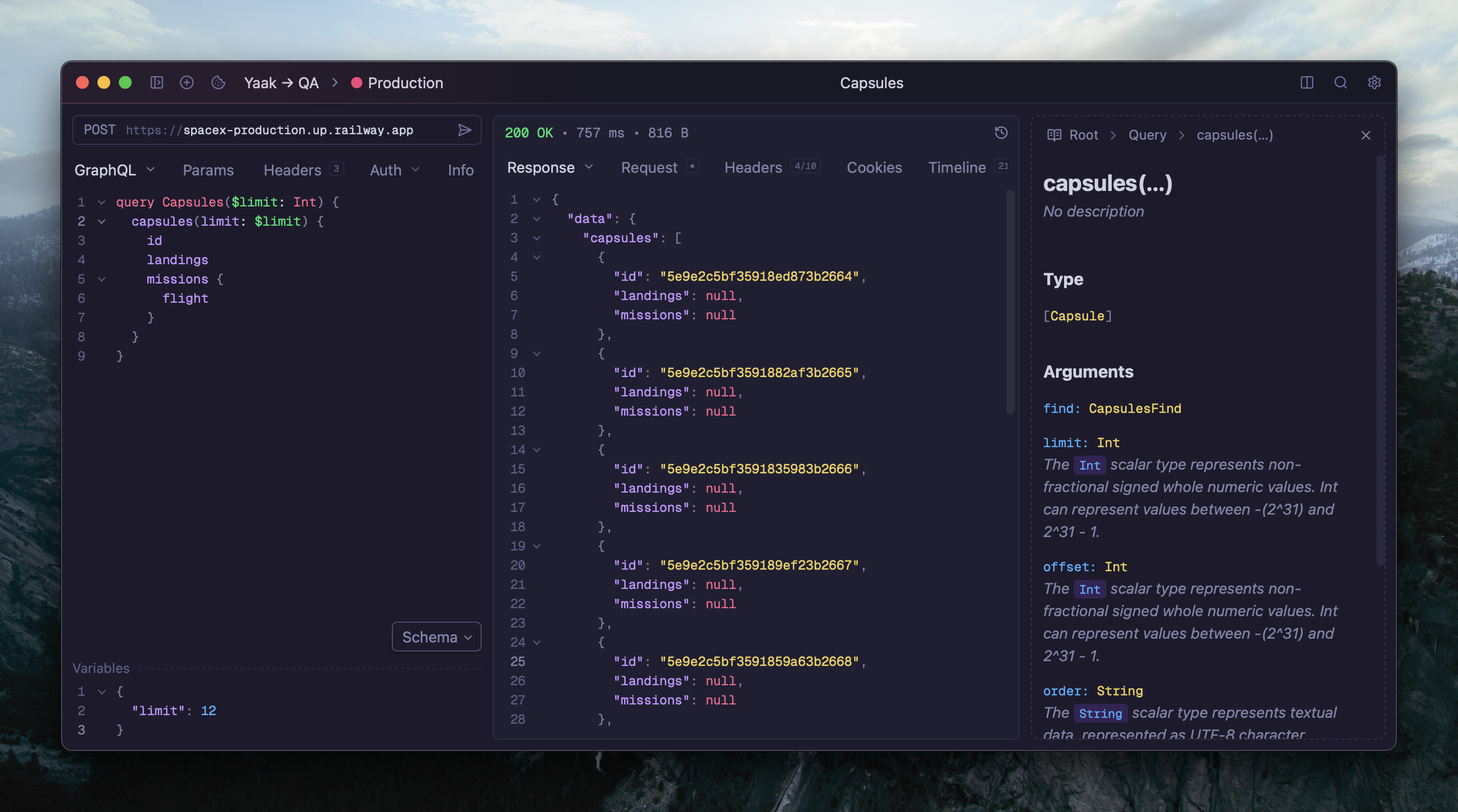
A GraphQL request in Yaak
Creating a GraphQL Request
Create a new request and select GraphQL from the request type dropdown. Enter your GraphQL endpoint URL—this is typically a single endpoint like https://api.example.com/graphql.
The editor provides two panels: one for your query/mutation and one for variables.
Writing Queries
Write queries in the left panel using standard GraphQL syntax:
query GetUser($id: ID!) {
user(id: $id) {
name
email
posts {
title
}
}
}
Add variables in the Variables panel as JSON:
{
"id": "123"
}
Click Send to execute. The response appears in the response panel with syntax highlighting.
Schema Introspection
Yaak fetches your GraphQL schema automatically via introspection. This enables autocomplete for field names, types, and arguments as you type.
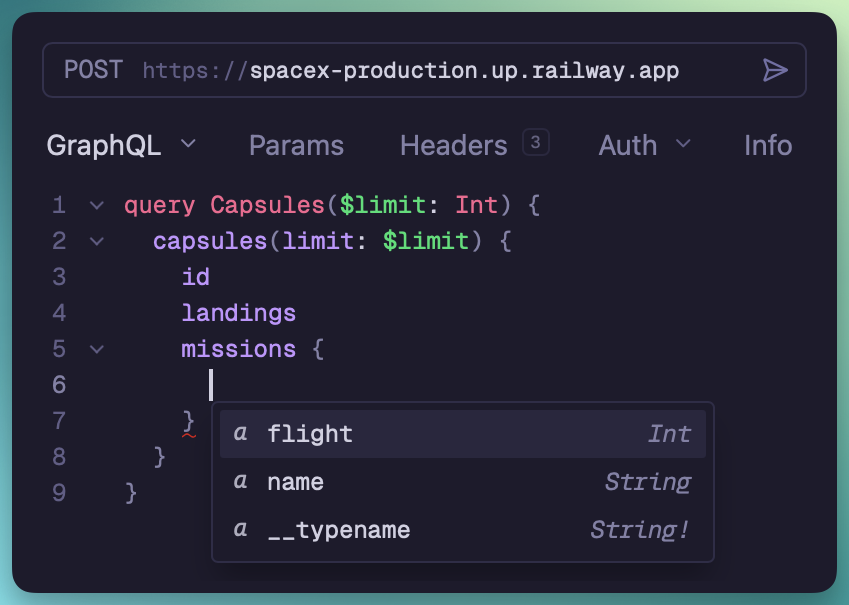
Autocomplete suggests fields from your schema
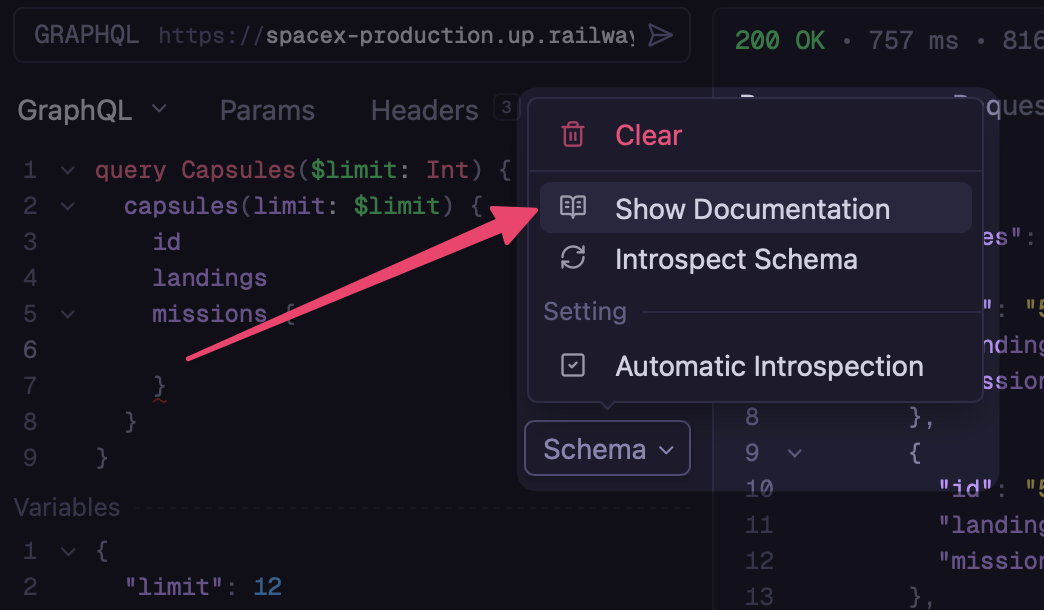
If introspection fails or you need to refresh the schema, click the schema menu button next to the URL bar. From there you can:
- Refresh schema - Fetch the latest schema from the server
- Clear schema - Remove the cached schema
- Disable auto-introspection - Prevent automatic schema fetching
Some servers disable introspection in production. Contact your API provider for schema files if needed.
Documentation Explorer
Browse your GraphQL schema without leaving Yaak. The Documentation Explorer shows all types, fields, queries, mutations, and their arguments.
Explore types and fields in the Documentation Explorer
Open the explorer from the schema menu or Command/Control-clicking type names in a query.
Mutations
Mutations use the same editor. Write the mutation and provide variables:
mutation CreatePost($input: PostInput!) {
createPost(input: $input) {
id
title
createdAt
}
}
{
"input": {
"title": "New Post",
"body": "Content here"
}
}
Headers and Authentication
Add custom headers in the Headers tab. Common uses include API keys and custom authentication headers.
Authentication works the same as HTTP requests. Bearer tokens, Basic auth, OAuth 2.0, and other methods configure in the Auth tab. Yaak adds appropriate headers automatically.
GraphQL requests support request inheritance—configure authentication once on a parent folder and all child requests inherit it.
Using Template Variables
URLs, queries, and variables support environment variables and template functions:
query GetUser {
user(id: "${[env.USER_ID]}") {
name
}
}
Variables panel:
{
"id": "${[env.USER_ID]}",
"timestamp": "${[now()]}"
}
Response Handling
Responses display with JSON syntax highlighting. GraphQL errors appear in the errors array of the response—Yaak shows these alongside any partial data returned.
Use response data in subsequent requests via request chaining. Reference response fields in template functions to build dynamic workflows.
Tips
- Use named queries for clarity and easier debugging in server logs
- Check the Documentation Explorer before writing queries to discover available fields
- Variables panel keeps queries reusable—avoid hardcoding values in the query itself
- Request inheritance reduces duplication for authentication across multiple GraphQL requests
Was this helpful?