Bearer Token Authentication
Authenticate requests with access tokens and API keys
Bearer Token authentication sends a token in the Authorization header. It’s the most common method for modern REST APIs, especially those using OAuth 2.0 access tokens or API keys.
How It Works
Bearer authentication adds your token to the Authorization header:
Authorization: Bearer <your-token>
The token is sent as-is without encoding, making it simple and efficient.
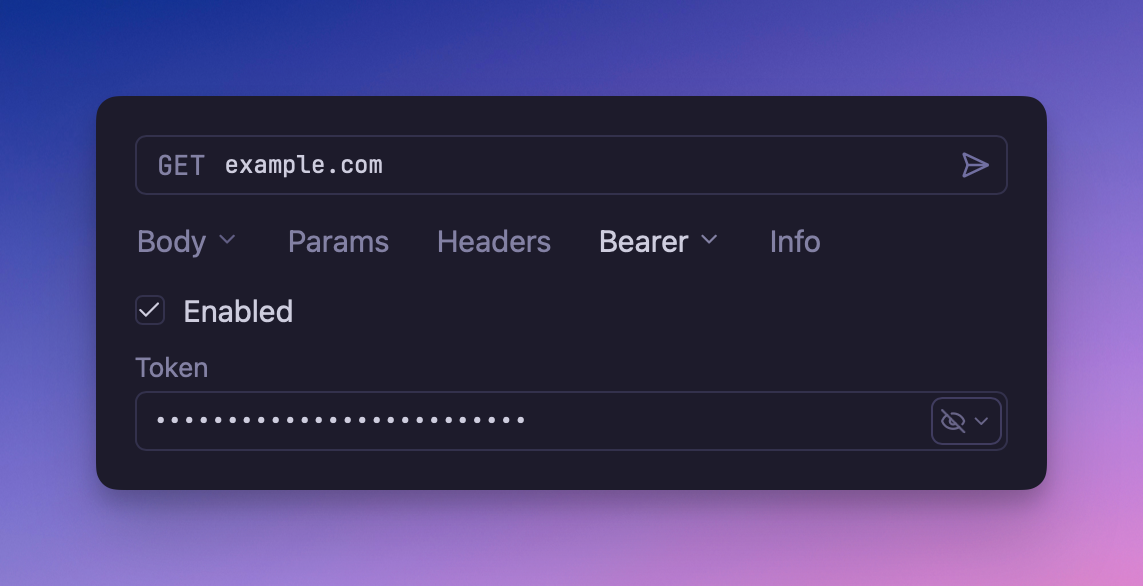
Configuration
Select Bearer Token from the Auth dropdown. Configure these fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Token | Your access token, API key, or other credential |
| Prefix | Header prefix (default: Bearer) |
The prefix lets you customize the authorization scheme. Some APIs use different prefixes like Token or ApiKey.
Usage
- Select Bearer Token from the Auth dropdown
- Paste your token
- Adjust the prefix if your API requires something other than
Bearer - Send your request
Use template variables for tokens that vary by environment:
Token: ${[env.API_TOKEN]}
Common Use Cases
Bearer tokens are used for:
- OAuth 2.0 access tokens from authorization flows
- API keys issued by service providers
- Personal access tokens from platforms like GitHub
- JWT tokens (though Yaak has dedicated JWT support)
Token vs OAuth 2.0
If your token comes from an OAuth 2.0 flow and needs automatic refresh, use the OAuth 2.0 auth type instead. Bearer Token auth is for static tokens that don’t expire or that you manage manually.
Troubleshooting
401 Unauthorized
- Verify your token is valid and not expired
- Check if you’re using the correct prefix
403 Forbidden
- Your token lacks the required permissions or scopes
- Request additional scopes from your OAuth provider
Invalid Token Format
- Ensure you’ve copied the complete token without truncation
- Remove any extra whitespace or newline characters
Was this helpful?